Services
Allergy skin testing
Skin Tests are used to confirm clinical sensitivity induced by aeroallergens, foods, and hymenoptera venom.
Indicated in following diseases:
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Food Allergy
- Atopic dermatitis
- Hymenoptera hypersensitivity
Factors affecting skin test:
- Age-infancy or old age
- Sex -no difference
- Race-whealing more in blacks
- Circadian rhythm peak in late evening
- Seasonal variation - Eg: pollen allergy
- Skin condition-skin eczema
- Other condition-diabetic neuropahthy
Method – Skin prick testing is done to demonstrate an allergic response to a specific allergen. SPT can help to confirm the presence of an allergy to pollen, food, dust, mites, moulds and animal dander’s. SPT is a simple, safe and quick test, providing results within 15-20 minutes. This will enable you to receive a diagnosis and management plan at your appointment.
The skin prick test introduces a tiny amount of allergen into the skin, eliciting a small, localized allergic response, in the form of a wheal (bump) and flare (redness) at the site of testing. These tests can be carried out on all age groups, including babies. The test allergens are selected following a discussion with your clinician and based on your history.
Prerequisites – The patient needs to avoid taking anti-histamines and certain other medications before the test.
Antihistamine for example cetrizine,loratidine,fexofenadine should be stopped at least 5 to 7 days before the testing. Tricyclic anti depressant( doxepine) and atypical antipsychotic drugs (ex.risperidone,olanzapine,ziprasidone) should be tapered down if required one week before the testing. Beta blockers should be stopped in all instances 24 hour before the testing.
Potential Risks of Non-Specialist Care
- Misinterpretation of test results
- Over diagnosis
- Mismanagement
- Over prescription of meds. and treatments
- Costly and unnecessary allergen avoidance
Patch test
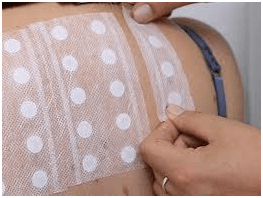
Allergy patch test is used to detect allergic contact dermatitis. This includes allergy to hair dyes, ingredients like fragrances and preservatives to cosmetics and medication ointments .
- If you suspect an allergy as a cause of your eczema such as to cosmetic ingredients or hair dye
- If you have eczema that is proving difficult to treat to ensure you are not allergic to ingredients of the treatment for your eczema
- If you have a work related eczema/dermatitis
Pulmonary function test
The tests determine how much air your lungs can hold, how quickly you can move air in and out of your lungs.
The tests can diagnose lung diseases, measure the severity of lung problems, and check to see how well treatment for a lung disease is working.
Lung function tests are done to:
- Determine the cause of breathing problems.
- Diagnose certain lung diseases, such as asthma or chronic obstructive. pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Evaluate a person’s lung function before surgery.
- Check the lung function of a person who is regularly exposed to substances. such as asbestos that can damage the lungs.
- Check the effectiveness of treatment for asthma and other lung diseases.
The testing may take from 5 to 30 minutes, depending upon how many tests are done.
Spirometry measures airflow. By measuring how much air you exhale, and how quickly, spirometry can evaluate a broad range of lung diseases. In a spirometry test, while you are sitting, you breathe into a mouthpiece that is connected to an instrument called a spirometer. The spirometer records the amount and the rate of air that you breathe in and out over a period of time.
How to Prepare for the Test?
- Do not eat a heavy meal before the test
- Do not smoke for 4 – 6 hours before the test
- you need to stop using bronchodilators or inhaler medications
- You may have to breathe in medication before or during the test.
Since the test involves some forced breathing and rapid breathing, you may have some temporary shortness of breath or lightheadedness. You breathe through a tight-fitting mouthpiece, and you’ll have nose clips.
Why the Test is performed? Pulmonary function tests are done to:
- Diagnose certain types of lung disease (such as asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema)
- Find the cause of shortness of breath
- Measure whether exposure to chemicals at work affects lung function
- Check lung function before someone has surgery
It also can be done to:
- Assess the effect of medication
- Measure progress in disease treatment
Normal Results
Normal values are based upon your age, height, ethnicity, and sex. Normal results are expressed as a percentage. A value is usually considered abnormal if it is less than 80% of your predicted value. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific
Test results
Different measurements that may be found on your report after spirometry include:
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- Forced vital capacity (FVC)
- Forced expiratory volume (FEV)
- Forced expiratory flow 25% to 75%
- Functional residual capacity (FRC)
- Maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV)
- Residual volume (RV)
- Peak expiratory flow (PEF).
- Slow vital capacity (SVC)
- Total lung capacity (TLC)
Abnormal results usually mean that you may have some chest or lung disease. Some lung diseases (such as emphysema, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and infections) can make the lungs contain too much air and take longer to empty. These lung diseases are called obstructive lung disorders.
Other lung diseases make the lungs scarred and smaller so that they contain too little air and are poor at transferring oxygen into the blood. Examples of these types of illnesses include:
- Extreme overweight
- Fibrosis of the lungs
- Lung cancer
- Sarcoidosis and scleroderma
Risks
The risk is minimal for most people. There is a small risk of collapsed lung in people with a certain type of lung disease. The test should not be given to a person who has experienced a recent heart attack, or who has certain other types of heart disease.
Considerations
Your cooperation while performing the test is crucial in order to get accurate results. A poor seal around the mouthpiece of the spirometer can give poor results that can’t be interpreted. Do not smoke before the test.
Absolute contraindication
- Cardiac surgery/Myocardial Infarction in the past 1 month
- Recent thoracic/abdominal/eye surgery in the past 1 month
- History of pulmonary embolism
- History of aneurysms abdominal/thoracic/ cerebral
- Presence of facial palsy/contractures
- Patient unwilling to perform the test. Activities that should be avoided before Pulmonary function testing
- Smoking tobacco in any form in the last 2-4 hrs
- Consuming tea/coffee/caffeinated drinks in the past 6 hr
- Heavy meal in past 4 to 5 hour
- Heavy exercise in the past ½ hour
- Bronchodilators: inhaled/oral
- Alcohol
- Lower respiratory tract infection in the past 15 days
Medication Wash out Restrictions:
- Short acting Beta2 Agonists (Eg. Salbutamol, Levosalbutamol): 6hrs
- Long Acting Beta2 Agonists (Eg. Formoterol, Salmeterol): 12hrs
- Long acting Antimuscarinic bronchodilators Tiotropium: 24hrs
- Long acting Theophyllines: 24-48hrs
- Short Acting Antimuscarinic bronchodilators .e.g. Ipratropium: 8hrs
- Inhaled steroids: 1hr
If above mentioned restrictions are not observed, then the spirometry readings may not be accurate and show false high levels. Moreover, bronchodilator reversibility will be unreliable.
Peak flow monitoring
A peak flow meter is a device that measures how well air moves out of the lungs. A peak flow meter is used to manage exacerbations. A peak flow meter is used for daily long-term monitoring. A peak flow meter guides therapeutic decisions in the home, school, clinician’s office, or ED
Use of Peak flow meter-
Peak flow meter is used to monitor your asthma control, as BP instrument is used to monitor hypertension and Glucometer is used to monitor diabetes control.
The peak flows are put into zones that are set up like a traffic light. Each zone determines what medications to use and what to do when the peak flow number changes.

